

Windows XP has its own zip wizard to help you do this. If you do not have. Download and open the Cygwin installer setup.exe from Cygwin's home. Note: if you.
This is what (i.e. My year) used to allow them to do their C++ programming on their laptops (running just Windows XP). The second intake of MOAC students actually ended up dual booting their laptops between Windows XP and Suse Linux (with the GCC tools running in Linux). So this may not be of much interest to the newer MOAC students. Programs are written in a text based language (e.g. Bendix autopilot.
C++) which must be translated into a program (machine code) for the computer to run. This is done using a compiler. You can buy C++ compilers to use on Windows (e.g. Microsoft Visual C++).
Also, the University Unix machines have the tools installed (which are free). These instructions are for installing (and subsidiary programs) on Windows XP. Cygwin is a Unix like environment that runs on top of windows, in particular it allows us to use the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC) to compile our programs. • • • • (for graphical unix programs) • (for drawing graphs and plotting data) • • You may also want to look at the official, in particular the section. Summary of Paths Windows C: Drive Windows - C: Cygwin - /cygdrive/c/ Windows D: Drive Windows - D: Cygwin - /cygdrive/d/ Cygwin folder: Windows - C: Cygwin Cygwin - / Cygwin setup folder, where we put Setup.exe and the downloaded files are kept by the setup program: Windows - C: Cygwin Setup Cygwin - /Setup/ Cygwin Home folder for username.
We made a shortcut to this on the desktop. Windows - C: Cygwin Home username Cywgin - /Home/ username/ or ~ (tilde) Windows XP Home folder for username: Windows - C: Documents and Settings username My Documents Cygwin - /cygdrive/c/Documents and Settings/ username/My Documents/.
If you are a Linux or Unix user, I am sure you will miss the terminal (and all the wonderful things you can do with command lines) in a Windows environment. Most of the time you won’t need to use the command prompt in Windows, and its user-interface is not as friendly either. However, if you have the need to use a terminal, Cygwin is the best tool for you. Let us see how to install and configure Cygwin in the Windows environment. What is Cygwin Cygwin is a free and open source software with tons of optional packages which lets you run and execute the age-old Unix-like commands right in your Windows system.
Do note that it can’t be used to run any Linux/Unix software though. Installing Cygwin To install Cygwin, head to the official site of and download the executable depending on your system preference (32-bit or 64-bit). The executable itself is small as it downloads all the required packages while installing the software. Once you have downloaded the Cygwin installer, launch the installer as the Administrator. You will be greeted with the welcome screen,;just click on the “Next” button to continue.
Here in this screen, select the radio button “Install from Internet” and click on the “Next” button. This option will download all the required packages for the installation and will store them in the local directory for future use. Here you can select the root directory for the Cygwin installation.
The default settings are fine unless you want to customize the installation directory and user access. Click on the “Next” button to continue. In this screen, you can select the local package directory where the downloaded files are stored. If you want to change it, go ahead and change the directory location by click on the “browser” button. Otherwise, click on the “Next” button to continue. Unless you are using some sort of HTTP proxy to access the internet, just leave the default option and click on the “Next” button to continue. Here you can select the download site from which you wish to download the required packages.
Unfortunately, Cygwin doesn’t provide any additional details like site location. So just select a random site and click on the “Next” button. As soon as you click on the “Next” button, Cygwin will show you all the available packages in categories. At this point, you can keep them at the default settings and click the “Next” button. If you ever want to add packages to your Cygwin installation, you can do so by running the installer as needed. Now Cygwin will download all the default packages and install them. The downloading and installing may take some time depending on your Internet speed and the selected server speed.
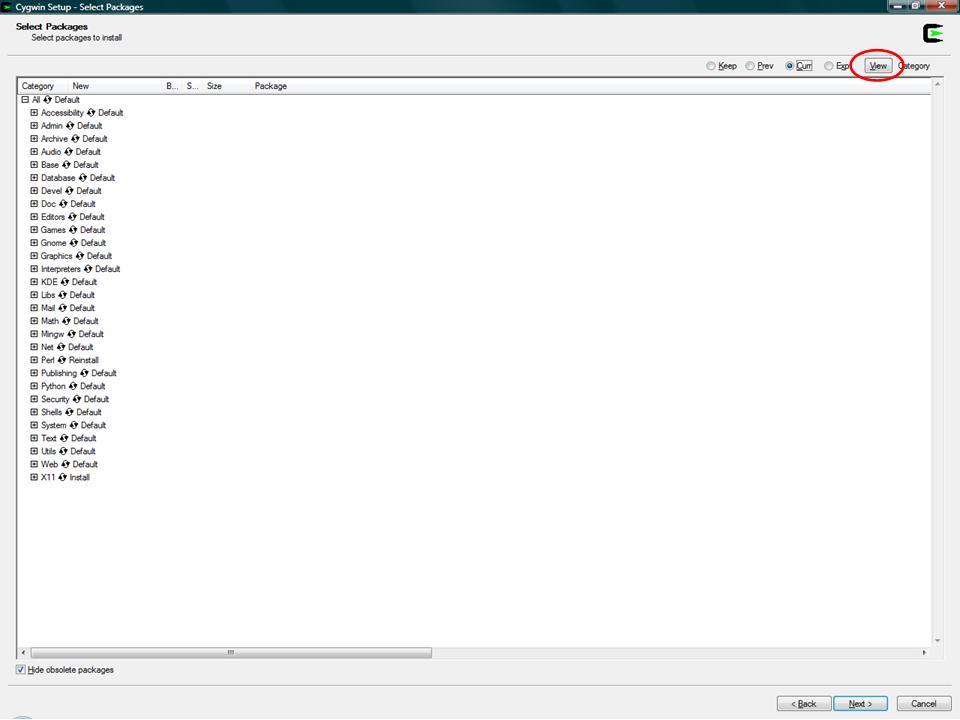
Once the installation is complete, you can start using Cygwin by launching it using the desktop shortcut or from the start menu. Alternatively, you can configure Cygwin to work with the normal Windows command prompt so you don’t have to launch Cygwin specifically. To do that, open up your Start menu, type “system” and select the option “System” in the control panel section. If you are using Windows 8, you can access the same section by pressing “Win + X” and selecting “System” from the power user menu. Click on the “Advanced System Settings” located on the left pane to open “System properties.” Click on the “Environmental Variables” button. Scroll down and select the variable “path” under the “system variables” and click on the “Edit” button.
- Author: admin
- Category: Category

Windows XP has its own zip wizard to help you do this. If you do not have. Download and open the Cygwin installer setup.exe from Cygwin's home. Note: if you.
This is what (i.e. My year) used to allow them to do their C++ programming on their laptops (running just Windows XP). The second intake of MOAC students actually ended up dual booting their laptops between Windows XP and Suse Linux (with the GCC tools running in Linux). So this may not be of much interest to the newer MOAC students. Programs are written in a text based language (e.g. Bendix autopilot.
C++) which must be translated into a program (machine code) for the computer to run. This is done using a compiler. You can buy C++ compilers to use on Windows (e.g. Microsoft Visual C++).
Also, the University Unix machines have the tools installed (which are free). These instructions are for installing (and subsidiary programs) on Windows XP. Cygwin is a Unix like environment that runs on top of windows, in particular it allows us to use the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC) to compile our programs. • • • • (for graphical unix programs) • (for drawing graphs and plotting data) • • You may also want to look at the official, in particular the section. Summary of Paths Windows C: Drive Windows - C: Cygwin - /cygdrive/c/ Windows D: Drive Windows - D: Cygwin - /cygdrive/d/ Cygwin folder: Windows - C: Cygwin Cygwin - / Cygwin setup folder, where we put Setup.exe and the downloaded files are kept by the setup program: Windows - C: Cygwin Setup Cygwin - /Setup/ Cygwin Home folder for username.
We made a shortcut to this on the desktop. Windows - C: Cygwin Home username Cywgin - /Home/ username/ or ~ (tilde) Windows XP Home folder for username: Windows - C: Documents and Settings username My Documents Cygwin - /cygdrive/c/Documents and Settings/ username/My Documents/.
If you are a Linux or Unix user, I am sure you will miss the terminal (and all the wonderful things you can do with command lines) in a Windows environment. Most of the time you won’t need to use the command prompt in Windows, and its user-interface is not as friendly either. However, if you have the need to use a terminal, Cygwin is the best tool for you. Let us see how to install and configure Cygwin in the Windows environment. What is Cygwin Cygwin is a free and open source software with tons of optional packages which lets you run and execute the age-old Unix-like commands right in your Windows system.
Do note that it can’t be used to run any Linux/Unix software though. Installing Cygwin To install Cygwin, head to the official site of and download the executable depending on your system preference (32-bit or 64-bit). The executable itself is small as it downloads all the required packages while installing the software. Once you have downloaded the Cygwin installer, launch the installer as the Administrator. You will be greeted with the welcome screen,;just click on the “Next” button to continue.
Here in this screen, select the radio button “Install from Internet” and click on the “Next” button. This option will download all the required packages for the installation and will store them in the local directory for future use. Here you can select the root directory for the Cygwin installation.
The default settings are fine unless you want to customize the installation directory and user access. Click on the “Next” button to continue. In this screen, you can select the local package directory where the downloaded files are stored. If you want to change it, go ahead and change the directory location by click on the “browser” button. Otherwise, click on the “Next” button to continue. Unless you are using some sort of HTTP proxy to access the internet, just leave the default option and click on the “Next” button to continue. Here you can select the download site from which you wish to download the required packages.
Unfortunately, Cygwin doesn’t provide any additional details like site location. So just select a random site and click on the “Next” button. As soon as you click on the “Next” button, Cygwin will show you all the available packages in categories. At this point, you can keep them at the default settings and click the “Next” button. If you ever want to add packages to your Cygwin installation, you can do so by running the installer as needed. Now Cygwin will download all the default packages and install them. The downloading and installing may take some time depending on your Internet speed and the selected server speed.

Once the installation is complete, you can start using Cygwin by launching it using the desktop shortcut or from the start menu. Alternatively, you can configure Cygwin to work with the normal Windows command prompt so you don’t have to launch Cygwin specifically. To do that, open up your Start menu, type “system” and select the option “System” in the control panel section. If you are using Windows 8, you can access the same section by pressing “Win + X” and selecting “System” from the power user menu. Click on the “Advanced System Settings” located on the left pane to open “System properties.” Click on the “Environmental Variables” button. Scroll down and select the variable “path” under the “system variables” and click on the “Edit” button.